Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-C7F5DB40-39D9-4EC4-A912-1EED65DC2F22
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-C7F5DB40-39D9-4EC4-A912-1EED65DC2F22
p?sytrd
Reduces a symmetric matrix to real symmetric tridiagonal form by an orthogonal similarity transformation.
Syntax
void pssytrd (char *uplo , MKL_INT *n , float *a , MKL_INT *ia , MKL_INT *ja , MKL_INT *desca , float *d , float *e , float *tau , float *work , MKL_INT *lwork , MKL_INT *info );
void pdsytrd (char *uplo , MKL_INT *n , double *a , MKL_INT *ia , MKL_INT *ja , MKL_INT *desca , double *d , double *e , double *tau , double *work , MKL_INT *lwork , MKL_INT *info );
Include Files
- mkl_scalapack.h
Description
The p?sytrd function reduces a real symmetric matrix sub(A) to symmetric tridiagonal form T by an orthogonal similarity transformation:
Q'*sub(A)*Q = T,
where sub(A) = A(ia:ia+n-1,ja:ja+n-1).
Input Parameters
- uplo
-
(global)
Specifies whether the upper or lower triangular part of the symmetric matrix sub(A) is stored:
If uplo = 'U', upper triangular
If uplo = 'L', lower triangular
- n
-
(global) The order of the distributed matrix sub(A) (n≥0).
- a
-
(local)
Pointer into the local memory to an array of size lld_a*LOCc(ja+n-1). On entry, this array contains the local pieces of the symmetric distributed matrix sub(A).
If uplo = 'U', the leading n-by-n upper triangular part of sub(A) contains the upper triangular part of the matrix, and its strictly lower triangular part is not referenced.
If uplo = 'L', the leading n-by-n lower triangular part of sub(A) contains the lower triangular part of the matrix, and its strictly upper triangular part is not referenced.
- ia, ja
-
(global) The row and column indices in the global matrix A indicating the first row and the first column of the submatrix A, respectively.
- desca
-
(global and local) array of size dlen_. The array descriptor for the distributed matrix A.
- work
-
(local)
Workspace array of size lwork.
- lwork
-
(local or global) size of work, must be at least:
lwork ≥ max(NB*(np +1), 3*NB),
where NB = mb_a = nb_a,
np = numroc(n, NB, MYROW, iarow, NPROW),
iarow = indxg2p(ia, NB, MYROW, rsrc_a, NPROW).
indxg2p and numroc are ScaLAPACK tool functions; MYROW, MYCOL, NPROW and NPCOL can be determined by calling the function blacs_gridinfo.
If lwork = -1, then lwork is global input and a workspace query is assumed; the function only calculates the minimum and optimal size for all work arrays. Each of these values is returned in the first entry of the corresponding work array, and no error message is issued by pxerbla.
Output Parameters
- a
-
On exit, if uplo = 'U', the diagonal and first superdiagonal of sub(A) are overwritten by the corresponding elements of the tridiagonal matrix T, and the elements above the first superdiagonal, with the array tau, represent the orthogonal matrix Q as a product of elementary reflectors; if uplo = 'L', the diagonal and first subdiagonal of sub(A) are overwritten by the corresponding elements of the tridiagonal matrix T, and the elements below the first subdiagonal, with the array tau, represent the orthogonal matrix Q as a product of elementary reflectors.
- d
-
(local)
Arrays of size LOCc(ja+n-1) .The diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix T:
d[i]= A(i+1,i+1), 0 ≤i < LOCc(ja+n-1).
d is tied to the distributed matrix A.
- e
-
(local)
Arrays of size LOCc(ja+n-1) if uplo = 'U', LOCc(ja+n-2) otherwise.
The off-diagonal elements of the tridiagonal matrix T:
e[i]= A(i+1,i+2), 0 ≤i < LOCc(ja+n-1) if uplo = 'U',
e[i] = A(i+2,i+1) if uplo = 'L'.
e is tied to the distributed matrix A.
- tau
-
(local)
Arrays of size LOCc(ja+n-1). This array contains the scalar factors of the elementary reflectors. tau is tied to the distributed matrix A.
- work[0]
-
On exit work[0] contains the minimum value of lwork required for optimum performance.
- info
-
(global)
= 0: the execution is successful.
< 0: if the i-th argument is an array and the j-th entry, indexed j - 1, had an illegal value, then info = -(i*100+j); if the i-th argument is a scalar and had an illegal value, then info = -i.
Application Notes
If uplo = 'U', the matrix Q is represented as a product of elementary reflectors
Q = H(n-1)... H(2) H(1).
Each H(i) has the form
H(i) = i - tau * v * v',
where tau is a real scalar, and v is a real vector with v(i+1:n) = 0 and v(i) = 1; v(1:i-1) is stored on exit in A(ia:ia+i-2, ja+i), and tau in tau[ja+i-2].
If uplo = 'L', the matrix Q is represented as a product of elementary reflectors
Q = H(1) H(2)... H(n-1).
Each H(i) has the form
H(i) = i - tau * v * v',
where tau is a real scalar, and v is a real vector with v(1:i) = 0 and v(i+1) = 1; v(i+2:n) is stored on exit in A(ia+i+1:ia+n-1,ja+i-1), and tau in tau[ja+i-2].
The contents of sub(A) on exit are illustrated by the following examples with n = 5:
If uplo = 'U':
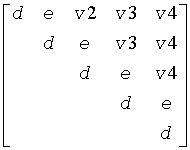
If uplo = 'L':
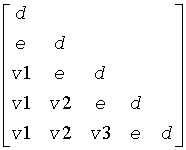
where d and e denote diagonal and off-diagonal elements of T, and vi denotes an element of the vector defining H(i).